Bachelor's degree program in Information Systems
The German-language Bachelor's degree course in Information Systems provides in-depth specialist knowledge of how business processes can be designed and challenges in companies solved with the help of computer science.
The Bachelor's degree course in Information Systems is a full-time, on-campus course with a standard period of study of six semesters (three years) and leads to a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degree. It starts in the winter semester. This can be followed by a Master's degree in Information Systems at our department.
Directly to the application in the TU Dortmund University campus portal
Study Plan
Below you will find a study plan for the start of the winter semester with its various modules. Please note the deadlines for seminar applications for economics modules.
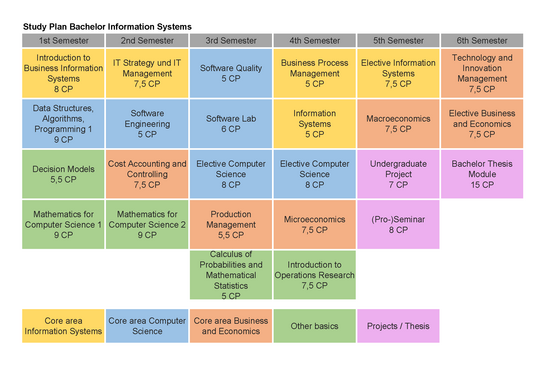
In courses offered by the departments of Business Administration and Economics and Computer Science, you will acquire knowledge of Information Systems, which, for example, deepens aspects of process automation, digital work and information management.
In the courses of the Department of Computer Science, you will learn the basics and specialized knowledge in several courses, which, for example, deepen aspects of intelligent systems and artificial intelligence or software, security and verification.
In the courses offered by the Department of Business and Economics, you will learn the basics and specialized knowledge in several courses, which, for example, deepen aspects of controlling, entrepreneurship or economics.
In courses offered by various departments, you will acquire knowledge of the mathematical foundations of computer science and decision models of operations research.
The curriculum above is an example. You can also customize your study plan. If you have any questions, please contact the Student Advisory Service at our department.
Frequently asked questions
With the knowledge acquired in the Information Systems course, not only can processes be optimized and problems solved in companies, but innovative new products and services and associated business models can also be designed.
The degree program offers you a balanced mix of compulsory and elective courses: In addition to a stable core of basic topics in Information Systems with the following content
- data management, process management and information management
the Bachelor's program also includes compulsory courses in
- computer science in the areas of software engineering and software construction,
- business and economics,
- and operations research as well as mathematical foundations for computer scientists
The latter offer you the ideal opportunity to acquire in-depth knowledge in the field of artificial intelligence in courses on machine learning, a major focus of education and research in Dortmund. In addition to the Department of Computer Science, the Lamarr Institute for Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence and the Research Center Trustworthy Data Science and Security conduct pioneering research in this field.
There are also numerous elective courses in Information Systems, Computer Science and Business and Economics to choose from. This range of subjects is supplemented by seminar-based and project-oriented modules in Information Systems.
In particular, the Bachelor's degree program in Information Systems covers the following three areas:
Data Management and Applied Artificial Intelligence
The role of data and information as a production factor in business operations is considerable. The field of action includes definitions of data, information and knowledge as well as the relationship of these concepts to each other and for the implementation of smart service and Industry 4.0 scenarios. Data also forms the basis for machine learning in applied artificial intelligence. A variety of topics are offered at TU Dortmund University under this collective term: In addition to mathematical fundamentals and advanced courses on deep and reinforcement learning, applied data science topics on natural language processing, industrial data science, and socio-technical topics on artificial intelligence in management and human-machine interaction are taught. This subject area is also closely related to computer science-related technical issues.
Business Engineering & Process Automation
Business engineering provides the theoretical basis for transformation projects. Business engineering describes the engineering design of business models and is a model-based and method-oriented approach to the transformation of companies. In order to transfer these concepts into professional practice, this requires the rethinking and reorganization of processes and the automation of these with so-called BPM systems or software robots in the sense of robotic process automation. Process mining can provide the basis for this. This subject area is particularly close to issues that form the core of Information Systems.
Digital transformation in business and society
The effects of digital transformation on companies and society are omnipresent and are changing rapidly. Analyses and design options must be discussed in a correspondingly adaptable and up-to-date manner. In this field, you will gain insights into digital technologies, their application in business models and the associated changes to processes and structures. Social aspects are also covered. The aim is to develop a sound understanding of the challenges and opportunities of digitalization. This subject area is also closely related to business, economic, and social science issues.
The German-language Bachelor's degree program in Information Systems at TU Dortmund University builds a bridge between the degree programs of the Department of Computer Science and the Department of Business and Economics. By studying Computer Science with a minor in Business and Economics and Applied Computer Science with a minor in Enterprise Computing, you only learn the basics of business processes, concepts, and methods.
Only the Information Systems degree program gives you not only a
- comprehensive training in core topics of business, economics and operations research,
- but also includes essential parts of the formal, technical training of computer science, especially in the field of software engineering.
This offer is supplemented by numerous courses in the core of Information Systems in the form of lectures, projects, and seminars.
You will not only apply the knowledge gained in lectures in tutorials, but also in the practical trainings integrated into the curriculum. In the software internship, you will work on your first software projects in groups to gain valuable programming experience and skills such as teamwork and project management. The undergraduate project also involves challenging tasks that are worked on in a group. As a rule, the focus here is on a small independent project.
Studying Information Systems opens up career opportunities in various sectors of the economy, including technology companies that act as providers of digital technology, user companies that use digital solutions, consulting firms and public administration. Another perspective is self-employment as an entrepreneur in your own start-up. It is also possible to pursue a doctorate, which opens up further career opportunities in industry and academia. Exemplary professional fields include IT management, IT consulting, IT entrepreneurship, process management, data analysis and artificial intelligence engineering. In view of the dynamic technological development, it is to be expected that new occupational fields will constantly emerge and existing occupational fields will change.
Example of IT consulting
IT consulting plays a key role, particularly in the planning, management, monitoring and implementation of larger projects for the digital transformation of organizations. IT consultants have in-depth business and technical expertise, on the basis of which they help their clients to master technological challenges and realize strategic competitive advantages. The tasks of IT consultants include analyzing the strategic and technical requirements of a company, recommending system improvements, planning and executing IT projects and supporting the implementation of new technologies. IT consultants often work in interdisciplinary project teams and must have strong communication skills in order to recognize and solve customer needs in different industries and companies and to justify decisions convincingly.
Example of process management
Process managers combine methodological, technical, and professional knowledge to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of business processes in organizations. On the one hand, they translate innovative business models, products and services into scalable operational value creation. On the other hand, business processes must also be carried out efficiently and to a high quality in order to ensure the company's success. Process managers have both target dimensions in mind and thus shape the core of operational value creation. Their tasks include the strategic planning of the process landscape, the definition and implementation of business processes, enabling the organization to carry out business processes and the analysis of process data as the basis for the continuous improvement of business processes. Process managers often work in interdisciplinary teams to combine professional and technical aspects into effective and efficient value creation
Example IT start-up
Digital entrepreneurs are generalists who combine methods from information systems and computer science with specialist knowledge from economics in order to develop and successfully market innovative digital products and services. This can be the case both for their own startup and on behalf of customers. Digital entrepreneurs develop their own start-ups based on practical problems (problem pull) or technological innovations (technology push). Digital entrepreneurs identify market opportunities for new digital solutions and business models, develop business plans, secure financing and lead teams to succeed with innovative products and services. To lead their company to sustainable success, they must manage risks, build strategic partnerships, further develop service portfolios and successfully scale companies, among other things.
Reference for examples: Rahmenempfehlung für Studiengänge in Wirtschaftsinformatik an Hochschulen (VHB/GI 2024)
After successfully completing your Bachelor's degree, the Master's degree course in Information Systems of the faculties of Computer Science and Business and Economics offers you the opportunity to specialize further in Information Systems and at the same time expand your opportunities on the job market.

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/storages/zentraler_bilderpool/_processed_/d/f/csm_Informatik_275ba5e5fc.jpg)

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/storages/zentraler_bilderpool/_processed_/1/b/csm_Figuren-nachdenklich_e2435967dd.jpg)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/storages/cs/_processed_/6/f/csm_teamwork1_e113f5f13b.png)
![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/storages/cs/_processed_/e/1/csm_header_ee496f74bf.png)